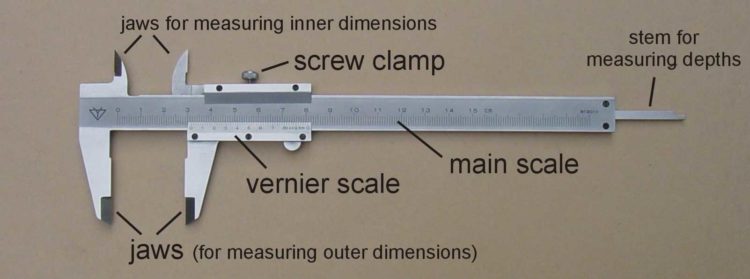
Construction and Main Parts The two upper jaws are the smaller jaws of the vernier that are used to measure the internal distances between two parallel sides of an object or an internal diameter. They are also known as the internal jaws.
Inside jaws: used to measure internal diameter of an object. Depth probe: used to measure depths of an object or a hole ( not shown in this model) Main scale: gives measurements in mm. Vernier gives measurements up to one decimal places in mm.
Thereof, What is vernier caliper and its uses?
The Vernier calipers are used to measure the inner and outer breadth of rods and domains and thickness of any sort of object accurately. The Vernier calipers can also be utilized to measure deepness of holes and objects which can be too hard to do with any other scale.
Also to know is, What are the main parts of a vernier caliper? Vernier scale or Nonius, outside jaws, inside jaws, knob, depth probe, and locking screw are some of the main components of the vernier caliper.
Subsequently, question is, What are the parts of vernier caliper and their functions? – Lower Jaws: The upper jaws are the most prominent feature of a vernier caliper. …
– Upper Jaws: The upper jaws are smaller in size and are attached to the upper portion of the vernier caliper. …
– Depth Rod: …
– Main Scale: …
– Vernier Scale: …
– Thumb Screw: …
– Lock Screw:
Also, What is the principle of vernier caliper?
The vernier caliper uses the principle of alignment of line segments to determine the more accurate reading. The length of the object to be measured is placed in between the two jaws of the vernier calipers. Certain graduation on the vernier scale gets signed with a reading on the main scale.
What is the main function of vernier caliper?
Measuring more precisely than could be done unaided when reading a uniformly divided straight or circular measurement scale
What are two parts of vernier scale?
– Internal jaws.
– External jaws.
– Main arm.
– Sliding arm.
– Depth measuring probe.
– Locking Screw.
What is the function of vernier caliper?
Measuring more precisely than could be done unaided when reading a uniformly divided straight or circular measurement scale
How do you read a vernier scale?
– Read the main scale. (Last whole or half mark increment visible)
– Read the secondary scale measurement. (Value of the scale that lines up with the center line of the main scale)
– Add the two measurements together.
How many parts are there in vernier caliper?
25 parts
How many divisions are there on its vernier scale?
10 divisions
What are the parts of vernier caliper?
– Internal jaws.
– External jaws.
– Main arm.
– Sliding arm.
– Depth measuring probe.
– Locking Screw.
What are the main parts of vernier caliper?
Vernier scale or Nonius, outside jaws, inside jaws, knob, depth probe, and locking screw are some of the main components of the vernier caliper.
Why is the caliper principle used?
Explanation: Caliper principle is used for the circular division or to divide a circular disc in number of divisions. Circular division deals with the continuous division of a Circle and measurement. The level of accuracy of circular division depends only on the precision of the equipment and the techniques used.
How many types of vernier callipers are there?
There are 8 different types of caliper available today. These include: inside caliper, outside caliper, divider caliper, oddleg caliper, micrometer caliper, Vernier caliper, dial caliper, and digital caliper.
How do you read a vernier caliper?
– Read the main scale. (Last whole or half mark increment visible)
– Read the secondary scale measurement. (Value of the scale that lines up with the center line of the main scale)
– Add the two measurements together.
What is the working principle of vernier caliper?
The vernier caliper uses the principle of alignment of line segments to determine the more accurate reading. The length of the object to be measured is placed in between the two jaws of the vernier calipers. Certain graduation on the vernier scale gets signed with a reading on the main scale.
Don’t forget to share this post 💖
References and Further Readings :