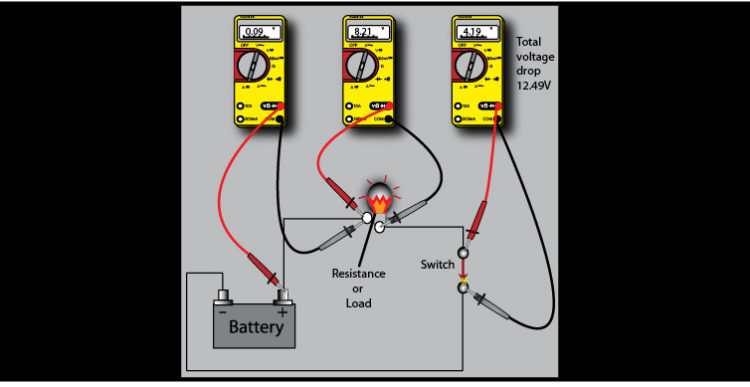
Voltage Drop testing is a method of electrical diagnosis that can quickly locate high-resistance problems in a circuit. Digital Volt/Ohmmeters (DVOM’s) can be used to measure the voltage drop across a load device or conductor. Voltage Drop is the loss of voltage caused by the flow of current through a resistance.
To do a voltage drop test, you create a load in the circuit that’s being tested. Then you use a digital volt meter (DVM) to measure the voltage drop across the live connection while it is under the load.
Thereof, When testing for a voltage drop always have the circuit on or off?
Voltage drop should be checked with the circuit loaded and a fully-charged battery. In best case scenarios, voltage drop on a power side or ground side to a component through all connectors, and connections should not exceed 0.1V or 100mV, however most times 0.2V or 200Mv is acceptable.
Also to know is, How do you check voltage drop with a multimeter? – Measure the voltage supplied by the battery pack. Next, measure the voltage across the resistor. …
– Measure the voltage across the resistor. Finally, measure the voltage across the LED. …
– Measure the voltage across the LED. …
– The voltage supplied by the battery is dropped across the resistor and the LED.
Subsequently, question is, What is a voltage drop test? Voltage Drop testing is a method of electrical diagnosis that can quickly locate high-resistance problems in a circuit. Digital Volt/Ohmmeters (DVOM’s) can be used to measure the voltage drop across a load device or conductor. Voltage Drop is the loss of voltage caused by the flow of current through a resistance.
Also, Where can a voltage drop test be performed?
Voltage drop testing is commonly done to check wires, connectors, and connections for excessive resistance. Normally, the voltage drop on the power feed side and ground side wires, connectors, and connections should not exceed 0.1V or 100mV.
How do you measure AC voltage drop?
What would cause a voltage drop?
Voltage drop is not caused by poor connections, bad contacts, insulation problems, or damaged conductors; those are causes of voltage loss. … You can have both voltage drop and voltage loss in any circuit. You can calculate the voltage drop by using any of several accepted voltage drop formulas.
What is the cause of voltage drop?
Voltage drop is not caused by poor connections, bad contacts, insulation problems, or damaged conductors; those are causes of voltage loss. … You can have both voltage drop and voltage loss in any circuit. You can calculate the voltage drop by using any of several accepted voltage drop formulas.
How do you test voltage?
Set a multimeter to measure voltage. Insert a probe into each slot and read the line voltage measurement. A properly working outlet gives a reading of 110 to 120 volts. If there is no reading, check the wiring and the outlet.
Where Does voltage drop occur?
A voltage drop in an electrical circuit normally occurs when a current passes through the cable. It is related to the resistance or impedance to current flow with passive elements in the circuits including cables, contacts and connectors affecting the level of voltage drop.
How do you measure voltage drop?
Voltage Drop testing is a method of electrical diagnosis that can quickly locate high-resistance problems in a circuit. Digital Volt/Ohmmeters (DVOM’s) can be used to measure the voltage drop across a load device or conductor. Voltage Drop is the loss of voltage caused by the flow of current through a resistance.
How do you perform a voltage drop test?
To do a voltage drop test, you create a load in the circuit that’s being tested. Then you use a digital volt meter (DVM) to measure the voltage drop across the live connection while it is under the load.
How do you test for voltage drop?
To check the entire circuit, connect the meter positive lead to a clean spot on the starter motor case and the meter negative lead to the negative battery post. Crank the engine and note the reading. The voltage drop on the negative side should be 0.3 volts or less.
What is the formula to find voltage drop?
Voltage drop of the circuit conductors can be determined by multiplying the current of the circuit by the total resistance of the circuit conductors: VD = I x R.
Is voltage drop good or bad?
How much voltage drop is acceptable? A footnote (NEC 210-19 FPN No. 4) in the National Electrical Code states that a voltage drop of 5% at the furthest receptacle in a branch wiring circuit is acceptable for normal efficiency. … It also means that the circuit has a resistance that does not exceed 0.4 ohms.
How do you prevent voltage drop?
The simplest way to reduce voltage drop is to increase the diameter of the conductor between the source and the load, which lowers the overall resistance. In power distribution systems, a given amount of power can be transmitted with less voltage drop if a higher voltage is used.
Can a loose connection cause voltage drop?
Excessive resistance on an electrical circuit can cause a restriction in current flow. … When corrosion, loose connections or other types of resistance restrict a circuit, volts and amps both drop. If volts drop, amps drop too.
Don’t forget to share this post 💖
References and Further Readings :